History Of D/IPR
History of Intellectual Property System in Cambodia
-
Background
In the Kingdom of Cambodia, intellectual property originated in the 1960s and '70s, and some brands were also protected during that period, such as the PERTUSSIN brand in the fifth chapter. The word 1973 was created in 1966, and the RIBENA brand is in chapters 5 and 32 with the application number 10318 in 1973. Unfortunately, Cambodia later experienced a severe civil war, which left the intellectual property sector abandoned for nearly two decades. With the Paris Agreement of October 23, 1991, Cambodia began to rehabilitate its national economic infrastructure, leading to the re-activation of the intellectual property sector. As a result, in 1991, the Trademark Office was established under the auspices of the Ministry of Commerce, which was responsible for the registration and protection of trademarks and received technical support and assistance from countries, especially intellectual property organizations. The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) is based in Geneva, Switzerland.
Department of Intellectual Property
In Cambodia, in 2019, there was a significant change in the leadership of the Department of Intellectual Property under the Ministry of Commerce, as mandated by the fourth sub-decree of the Kingdom of Cambodia. Prior to this, the Department of Foreign Trade had oversight of intellectual property protection. The Department of Intellectual Rights now holds responsibility for:
- Study, analyze, and recommend intellectual property policies to the Minister of Commerce and the Government of Cambodia.
- Coordinate and draft laws and regulations on intellectual property rights.
- Coordinate and facilitate cooperation and assistance in the field of intellectual property with the international community.
- Oversee the three areas of intellectual property in Cambodia, act as the focal point of intellectual property, and coordinate all intellectual property issues with the relevant ministries.
- Promote the proper and effective protection of intellectual property rights through various dissemination methods.
- Implement all obligations set out in agreements and conventions.
From 1994 to 1998, the Department of Intellectual Property registered 7,055 trademarks, including 198 local trademarks and 6,855 foreign trademarks.
Mark registered between 1994 and 1998: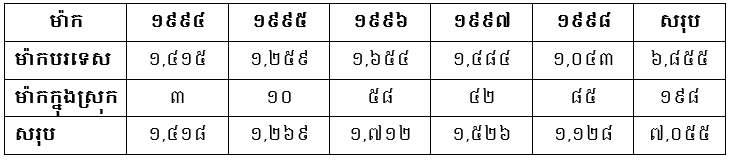
Management Committee of the three sections of intellectual property
Although intellectual property was a relatively new concern for the Kingdom of Cambodia, the Department of Intellectual Property made significant strides under the leadership of Mr. Ly Phanna from 1997 to 2004. With technical assistance from the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), the department focused on capacity building through both local and international training programs. These efforts included short-term training sessions, national seminars, and participation in international forums dedicated to intellectual property. Additionally, the department received support in terms of technical equipment. During this period, the department played a crucial role in trademark registration and protection, both domestically and internationally. Under Mr. Ly Phanna's guidance, who later served as the Director General of the Ministry of Commerce and the Minister of Commerce of the Phnom Penh Special Economic Zone, the department witnessed notable achievements. These accomplishments included raising public awareness, enhancing law enforcement activities, and fostering collaboration with national and international stakeholders. Despite these achievements, the department faced challenges. It operated with a limited staff of 40 employees and had two subordinate offices: the trademark registration office and the media and information office. The volume of intellectual property work was relatively modest, with the department processing approximately 1,500 to 2,000 trademark applications annually, primarily consisting of foreign trademarks. Moreover, the registration of brands averaged about 1,500 per year. The department's resources were further constrained by the use of typewriters for document processing, highlighting the technological limitations at the time.
Nearly two years later, at the request of the Ministry of Commerce and for the purpose of a single national intellectual property policy, the Royal Government of Cambodia issued Decree No. 16 dated February 22, 1999, establishing the “Management Committee. The three sections of intellectual property ”are chaired by the Minister of Commerce, and the Department of Intellectual Property is chaired by the Secretariat of the Committee of Ministers of the Ministry of Industry, Mines, and Energy, with the Minister of Culture and Fine Arts and the Ministry of Information as members. The duties of this committee are:- Accelerate the drafting of all laws and regulations related to the field of intellectual property to fulfill Cambodia's obligation to join the World Trade Organization.
- Coordinate all intellectual property issues between the relevant ministries above.
After seven years as Director of the Department of Intellectual Property, Mr. Ly Phana was promoted to Deputy Director General of Technical Affairs of the Ministry of Commerce, and then in early 2008 he was promoted to Director General and Representative of the Minister of Commerce. Services in Phnom Penh Special Economic Zone. Mr. Va Rutsan, who was the Deputy Director of the Intellectual Property Department at the time, also took over as the Director of the Intellectual Property Department until now, and he is also an advisor to the Ministry of Commerce and Industry. She is also chair of the Secretariat of the National Committee for the Management of Intellectual Property. Thanks to the hard work and ingenuity of His Excellency Mr.Va Ruthsan, the Department of Intellectual Property has grown tremendously from year to year, receiving double or triple trademark registration applications. There are about 3,500 to 4,000 trademarks and about 3,000 registered trademarks per year. As a result, the revenue generated from the payment of trademark registration fees has also increased significantly.
Along with this growth, the cooperation between the Department of Intellectual Property and overseas development partners has been further strengthened by receiving technical assistance, both legal and material, which has led to the department's reputation being recognized. On the international stage, such as the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), the EU-ASEAN Cooperation on Intellectual Property Protection (ECAPII), the Japan Patent Office (JPO), the Office of Trademarks, and the United States Patent (USPTO),
In addition, human resources and departmental size need to be expanded. His Excellency President Mr. Va Ruthsan devised a way by submitting a request to the Minister of Commerce for additional staff and four additional offices to suit the situation at the time. On September 19, 2007, the Minister issued a proclamation on the organization and functioning of the Department of Intellectual Property, deciding to establish four more offices:- Post-Registration trademark Office.
- Office of trademarks, geographical indications, and confidential information.
- Dispute Office.
- Office of Cooperation and Legal Affairs.
National Committee for Management of Intellectual Property
Eight years after Cambodia became a member of the World Intellectual Property Organization, the readiness to implement the TRIPS Agreement has been strengthened in line with the Royal Government's Phase II Rectangular Strategy: "Strengthening the implementation of intellectual property rights law." In order to consolidate policy-making, enforcement of intellectual property law, and technical assistance, the Royal Government of Cambodia has issued a sub-decree on "Establishment of the National Committee for the Management of Intellectual Property" No. 142, dated September 18, 2008, replacing the old decision of 1999 with the Department of Intellectual Property of the Ministry of Commerce as the Secretariat. This committee is responsible for formulating a national policy on intellectual property, strengthening cooperation between agencies or institutions, disseminating new laws and regulations, and acting as a focal point for receiving technical assistance. The committee is chaired by the Minister of Commerce and has 13 other ministries as members. This National Committee has additional duties beyond the three committees of the Intellectual Property Administration to cooperate in disseminating the intellectual property law to civil servants, students, and educational institutions, in cooperation with competent authorities and the courts to prevent intellectual property infringement, and to study the agreement. And international treaties to find strengths and weaknesses.
Based on the tasks set out in the sub-decree, the Department of Intellectual Property, the Secretariat of the National Committee for the Management of Intellectual Property, has collaborated with ECAPIII to develop a 39-point action plan with the specific goal of creating a strong national intellectual property system. To protect intellectual property, manage and enforce the law in accordance with international intellectual property standards, and support the Royal Government's business development goals. After the Department, in particular HE President Va Rutsan, sought the support of overseas development partners, 21 activities were supported by the World Intellectual Property Organization and the World Bank. The director then added new ideas to the remaining 52 activities. Currently, the Department of Intellectual Property is moving forward by drafting a sub-decree on strengthening the implementation of intellectual property rights, education, and dissemination.Legal framework
Since national unity in 1991, Cambodia has regained its intellectual property rights, as many foreign traders and investors have asked the Ministry of Commerce and the Council of Ministers to officially retain their trademarks. They. The main concept of the Cambodian Intellectual Property Policy from 1991 to 2003 was to develop laws and regulations on trademarks, patents, and copyright to comply with its obligations under the TRIPS Agreement of the World Trade Organization. The second phase of the Royal Government of Cambodia's Rectangular Strategic Policy is to bring the intellectual property law in line with the country's development needs, especially in the fields of education, agriculture, and health. The Royal Government of Cambodia considers the protection of intellectual property to be important for promoting economic development, promoting foreign investment and technology transfer, and facilitating Cambodia's integration into the world economy.
Initially, the protection of Cambodia's intellectual property was based on Articles 47 and 48 of the provisions relating to the laws and criminal procedure of the judiciary, which were applicable in Cambodia during the transitional period of the United Nations Transitional Authority in Cambodia. UNTAC: United Nations Transitional Authority in Cambodia) dated September 10, 1992; Proclamation No. 368 of the Ministry of Commerce dated December 15, 1997; Proceedings of the Department of Intellectual Property Intended to ensure the protection of intellectual property rights. Paved the way for WTO accession in 2004. In this proclamation, the Department has the right to register and provide trademark certificates and signage services to traders and investors, both domestic and foreign, as well as to resolve all issues arising from this registration. On February 14, 2000, the Ministry of Commerce and the Ministry of Industry, Mines, and Energy issued a Memorandum of Understanding to transfer the duties of managing and registering the protection of local trademarks. Under the control of the Ministry of Industry, Mines, and Energy, under the authority of the Ministry of Commerce. Therefore, all issues related to the brand are the sole responsibility of the Ministry of Commerce.
Cambodia currently has four intellectual property laws:- Trademark law and acts of dishonest competition, promulgated on February 7, 2002, specify the duties of the Ministry of Commerce for trademarks. The Ministry of Commerce does not exclusively control all issues related to intellectual property.
- The law on patents, utility models, and industrial drawings is regulated by the Ministry of Industry, Mines, and Energy. This law was promulgated on January 22, 2003, while the Ministry was preparing regulations such as sub-decrees or prakas for the implementation of this law.
- The Copyright and Related Rights Act, promulgated on March 23, 2003, is governed by the Ministry of Culture and Fine Arts for the protection of this right.
- The Law on Plant Variety Control and Plant Breeder's Rights was adopted on April 8, 2008, under the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries.
Last updated on: July 29, 2024



